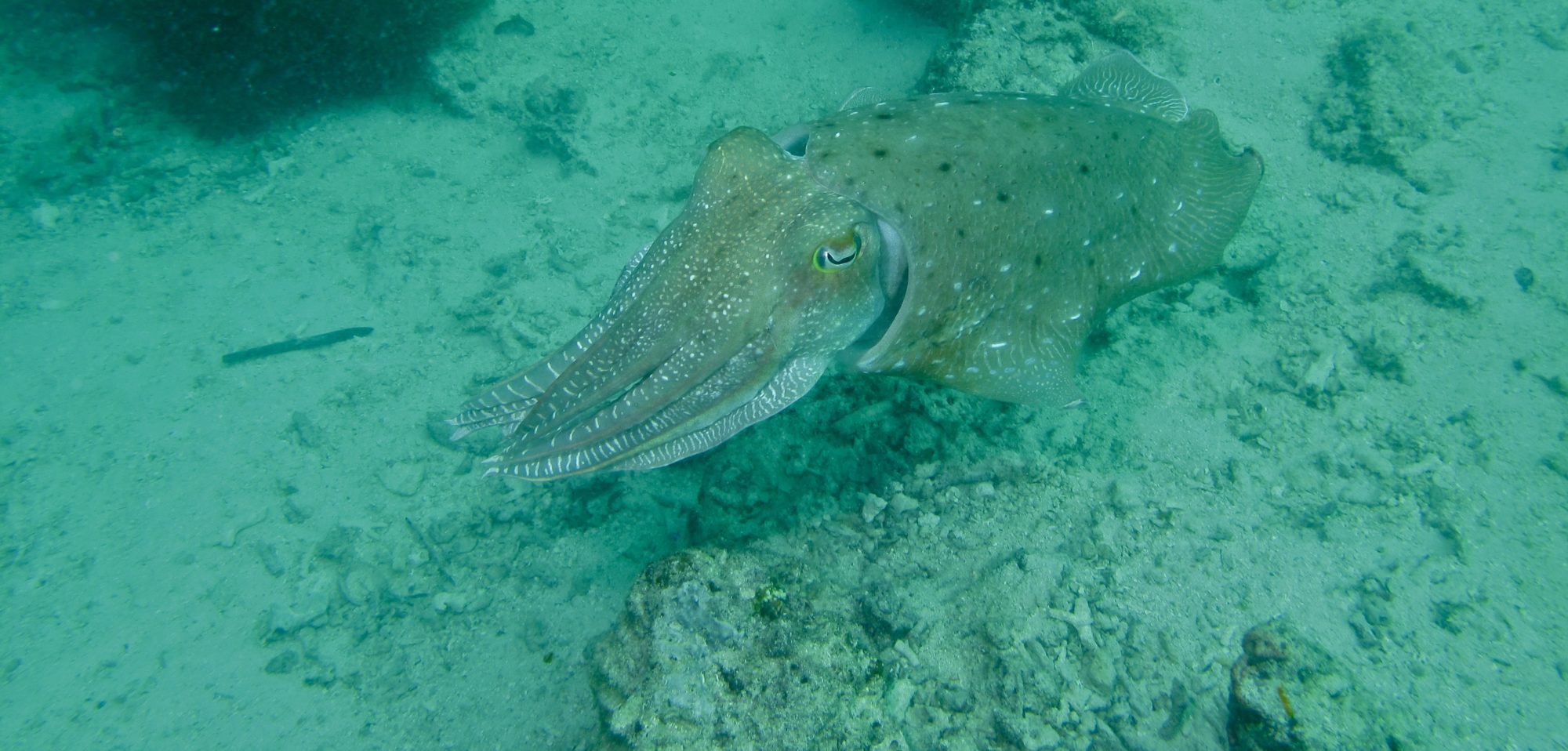
Until 1938 they thought the coelacanth was extinct. 50 years later Erdmann found another species of coelacanth. The Japanese emperor discovered a rare comb jelly in 1941. This jelly like creature lives attached to a rock in the middle of the sea and feeds in the most extraordinary way. It throws out long sticky filaments which catch tiny prey drifting by in the water. The sea lily looks just like those found in fossils dating back 400000000 years. It has changed very little over the millennia. When something approaches it it starts waving it’s arms. It may look like a plant but it is in fact an animal. And if In danger it will resort to a remarkable strategy. It detaches itself and uses its feathery arms to crawl over the sea floor in search of a safer spot. 400000000 years ago thick carpets of these strange creatures covered the sea floor forming spectacular underwater meadows. The warm shallow waters were rich in plankton and there were few large predators. The Nautilus, an ancient relative of the Squid and Octopus and Cuttlefish hunted small marine invertebrates such as trilobites. Over time more formidable predators began to appear. Primitive Sharks, and huge armored fish with powerful jaws and the ability to swim swiftly, these formidable hunters ruled the shallow seas. A lot of the prehistoric sea creatures became extinct. sea lilies, and some other species survived and took shelter in the deeper ocean. During the age of the dinosaurs even bigger and more ferocious predators began to appear in the shallow seas. Large swimming reptiles like the plesiosaur. Those who lived in deeper waters were largely unaffected by the struggle for survival. If you want to get the full version, this is the link to the documentary by David Attenborough : https://youtu.be/el9OJGEGWa8